Inductive proximity sensors Characteristics
Operating principle and purpose
Inductive proximity sensors are used to switch DC and AC electrical circuits. They act on the basis of induction - if a metal piece is brought to the active surface, the output switches over - the electric circuit opens or shuts. When there is metal in front of the active part of the sensors, the output indicator is on. Lack of physical contact between object and inductive proximity sensors ensures their high reliability and long-lasting exploitation. Inductive sensors are used for automatic transfer lines, metal cutting, textile, wood working, packaging and other machines. They are used in automation in solving problems in conditions of high dust, moisture, lubricants, oils, vibrations and long-term operation.
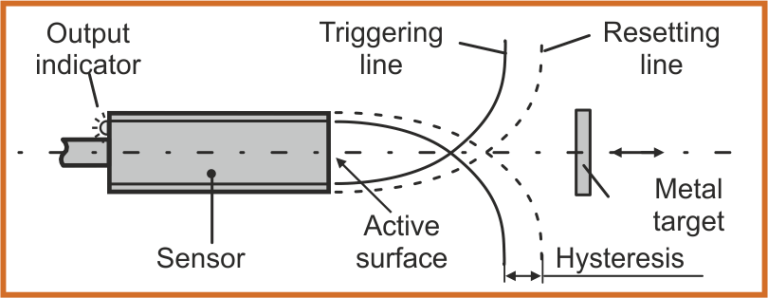
Hysteresis
Hysteresis denotes the distance between the triggering line with target approaching the sensing surface and the resetting line with target withdrawing from the sensing surface of the sensor. The value is expressed as a percentage of the nominal switching distance (Sn).
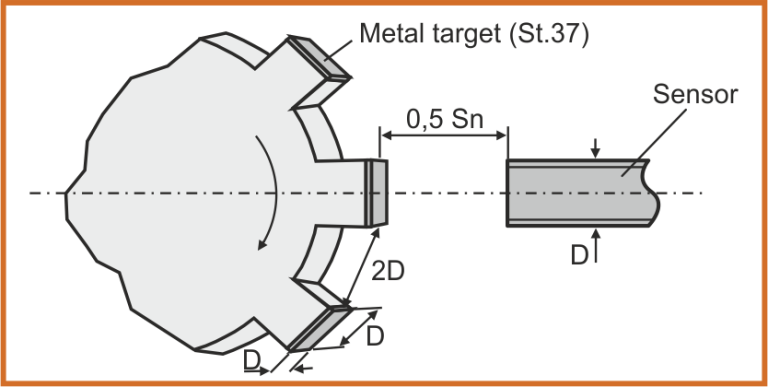
Nominal switching distance / Sn /
Sn - nominal switching distance, measured by the help of target, made from steel 37, 1 mm thick, in a form of square with a side equal in length to the diameter of the active surface of the sensor.
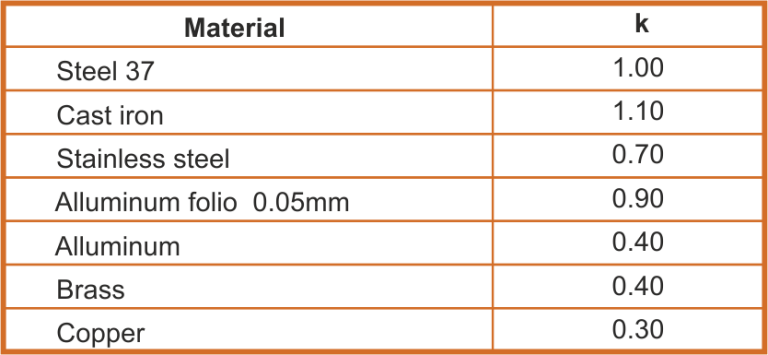
Coefficient of correction / k /
Switching distance S of the inductive proximity sensors varies according to the material of the target.
S = k . Sn
Maximal switching frequency / f max /
Maximal switching frequency denotes the maximum possible number of switching operations, the sensor can perform per second. The measurement is shown in figure:
Technical characteristics
| Stability to vibrations | 10...80Hz / 0,15mm |
| Stability blow | 9,8g |
| Stability electromagnetic influences | 400A/m (50Hz) |
| Insulation resistance | 50MΩ (1000V) |
Technical materials
| Housing-metallic | CuZn (brass - chromium plated) |
| Housing-metallic | Al (aluminum) |
| Housing-plastic | PVC (polyvinyl-chloride) |
| Sensing surface | PA (polyamide) |
| Cable shoe | ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) |
| Nut-metallic | CuZn (brass - chromium plated) |
| Nut-plastic | PA (polyamide) |
| Cable | PVC (polyvinyl-chloride) |
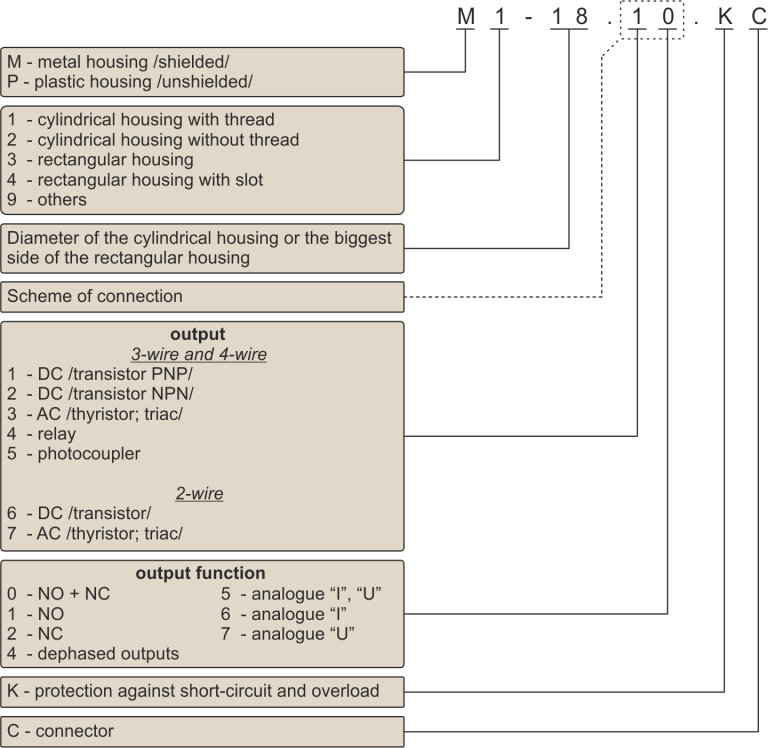
Type designation of inductive sensors
Rules for installation of inductive sensors
a) installation of unshielded inductive sensors (with plastic housing)
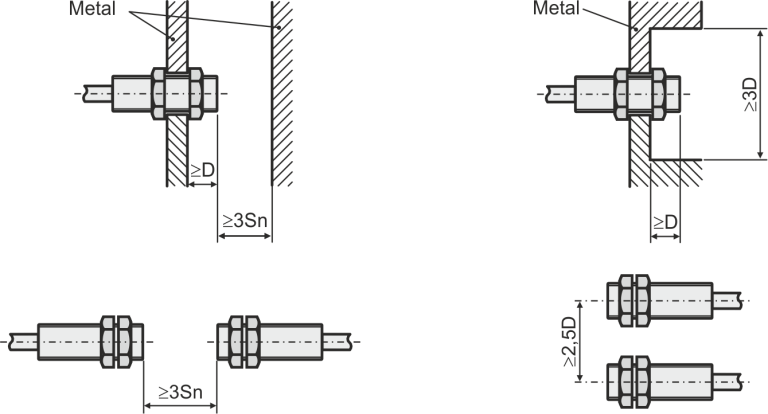
b) installation of shielded inductive sensors (with metallic housing)

Sn - nominal switching distance
D - diameter of the sensor
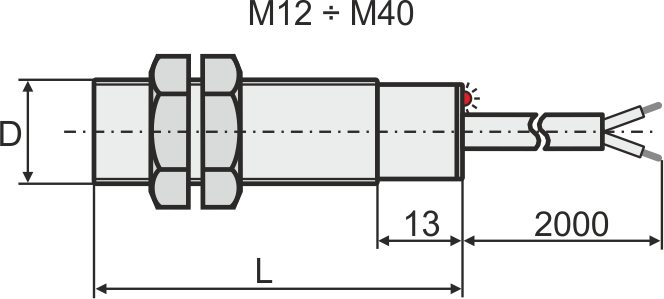
Overall dimensions of cylindrical inductive sensors